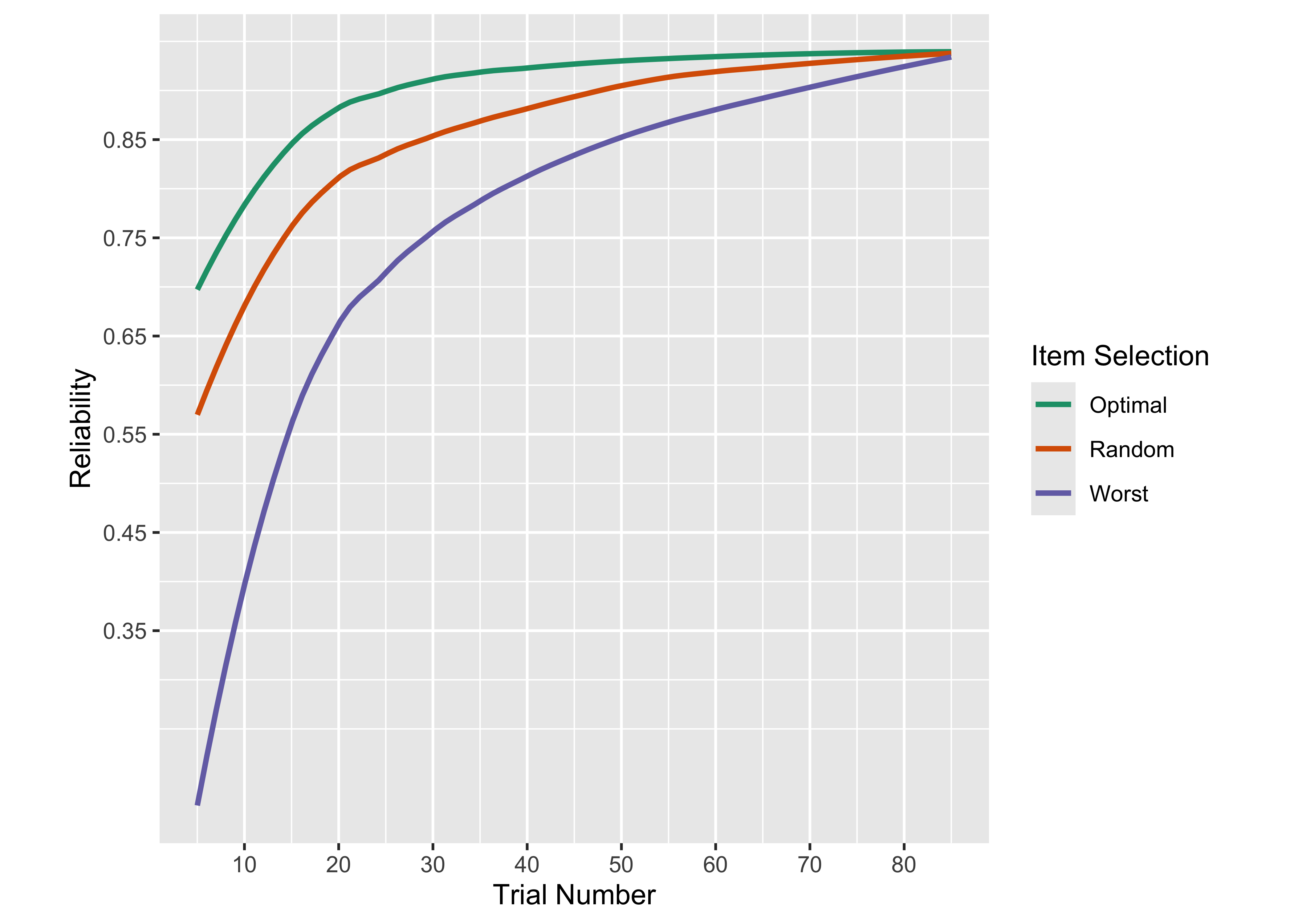
Reliability of calibration sample
A Rasch model was fit to the ROAR-Letter calibration sample (see Table 19.1 and Table 8.1). All ROAR-Letter items fit the model well (see Chapter 4 for fit criteria). Calibration data was obtained from 5187 students who took ROAR-Letter. Two versions of ROAR-Letter were administered: 1086 students took the full, 88 item version (with unlimited time) and 3604 students took a shorter version consisting of 10 letter names and up to 36 letter-sound items, with testing time to limited 5 minutes. On average the latter group completed 45 items (10 letter-name and 35 letter-sound items). Based on this IRT model, overall marginal reliability for ROAR-Letter was calculated to be 0.88 using 25 trials from each participant. Figure 19.2 shows the upper and lower bounds on reliability as a function of the number of items that a participant completes.
25 Trials
Item selection: Fisher information
Marginal reliability = 0.86
Reliability of computer-adaptive ROAR-Letter
A computer-adaptive version of ROAR-Letter is planned for release in fall 2024 and will be more efficient and reliable with fewer items. Using data from the calibration sample, we ran a CAT simulation as described in (Ma et al. 2023) to determine the final item selection criteria that would maximize reliability in the fewest number of trials (Figure 19.2). After selecting 25 trials as the most efficient number, we simulated a 25-trial computer adaptive test using participant responses.
Reliability (\(\rho_{xx^\prime}\)) is computed based on the estimated variance of \(\hat{\theta}\) relative to the estimated standard error (\(\widehat{SE}(\hat{\theta})^2\)) using Equation 23.1.
Table 19.2 reports marginal reliability by grade, based on a 25-item simulation of an optimal item selection algorithm using participant data. To ensure that ROAR-Letter is fair and equitable for different demographic groups, we also report reliability by gender Table 19.3, eligibility for free and reduced price lunch Table 19.4, English learner status based on state of California designations (Table 19.5), primary langauge spoken ?tbl-letter-primarylanguage-reliability, special education Table 19.7, ethnicity Table 19.8, and race Table 19.9.
References
Ma, Wanjing A, Adam Richie-Halford, Klint Burkhardt Amy and Kanopka, Clementine Chou, and Jason D Domingue Benjamin and Yeatman. 2023. “ROAR-CAT: Rapid Online Assessment of Reading Ability with Computerized Adaptive Testing.”