| ROAR Measure | ROAR Administration | N | Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|
| ROAR Word | Fall 2021 | 115 | 0.696 |
| ROAR Word | Spring 2022 | 117 | 0.659 |
| ROAR Word | Fall 2022 | 120 | 0.675 |
| ROAR Word | Spring 2023 | 136 | 0.749 |
| ROAR Word | Fall 2023 | 156 | 0.742 |
| ROAR Phoneme | Spring 2022 | 72 | 0.413 |
| ROAR Phoneme | Fall 2022 | 114 | 0.533 |
| ROAR Phoneme | Spring 2023 | 129 | 0.564 |
| ROAR Phoneme | Fall 2023 | 157 | 0.516 |
| ROAR Sentence | Spring 2023 | 120 | 0.709 |
| ROAR Sentence | Fall 2023 | 155 | 0.693 |
31 Predictive Validity
31.1 Background: Published studies
Predictive validity of ROAR Foundational Reading Skills (see Section 10.1 for additional information on ROAR Foundational Reading Skills) was first reported by (Gijbels, Burkhardt, and Ma 2024). Gijbels, Burkhardt, and Ma (2024) examined the classification accuracy of ROAR Foundational Reading Skills administered in 1st grade for classifying students who were deemed “at risk” for reading difficulties based on the Fountas and Pinnell (F&P) Benchmark Assessment 8 months later in the fall of 2nd grade. This study included N=130 1st grade students from a public school in California. Students completed ROAR Foundational Reading Skills measures in their classroom and F&P Benchmark Assessments were administered by their classroom teachers. A Generalized Additive Model (GAM) (S. Wood and Wood 2015; S. N. Wood 2017) based on ROAR-Phoneme achieved an AUC=0.70, ROAR-Word achieved and AUC=0.83, and a GAM with ROAR-Phoneme and ROAR-Word achieved an AUC=0.84. The prediction accuracy of ROAR-Phoneme and ROAR-Word for reading skills assessed the following school year with individually-admininstered assessments demonstrated the promise of ROAR as a quick and automated screener.
We ran 5 additional studies to assess the predictive validity of ROAR Foundational Reading Skills. For each study we report Area Under the Curve (AUC), Sensitivity, and Specificity as measures of classification accuracy and Pearson’s \(\rho\) as a measure of prediction accuracy for continuous criterion measures.
31.2 Study 1 (Grades 1-3): Two-year longitudinal study with Woodcock Johnson’s Basic Reading Skills (BRS) as the criterion
In a large California school district, all the 1st grade classrooms were administered ROAR Foundational Reading Skills measures three times per year and were followed longitudinally for 2 years. In the fall of 3rd grade, each student was individually administered the Woodcock Johnson Basic Reading Skills (WJ BRS) Composite Index. Based on this criterion measure, we assessed sensitivity and specificity of ROAR at each timepoint for predicting students who were classified as struggling readers with indications of dyslexia. Additionally we report prediction accuracy based on BRS as a continuous measure.
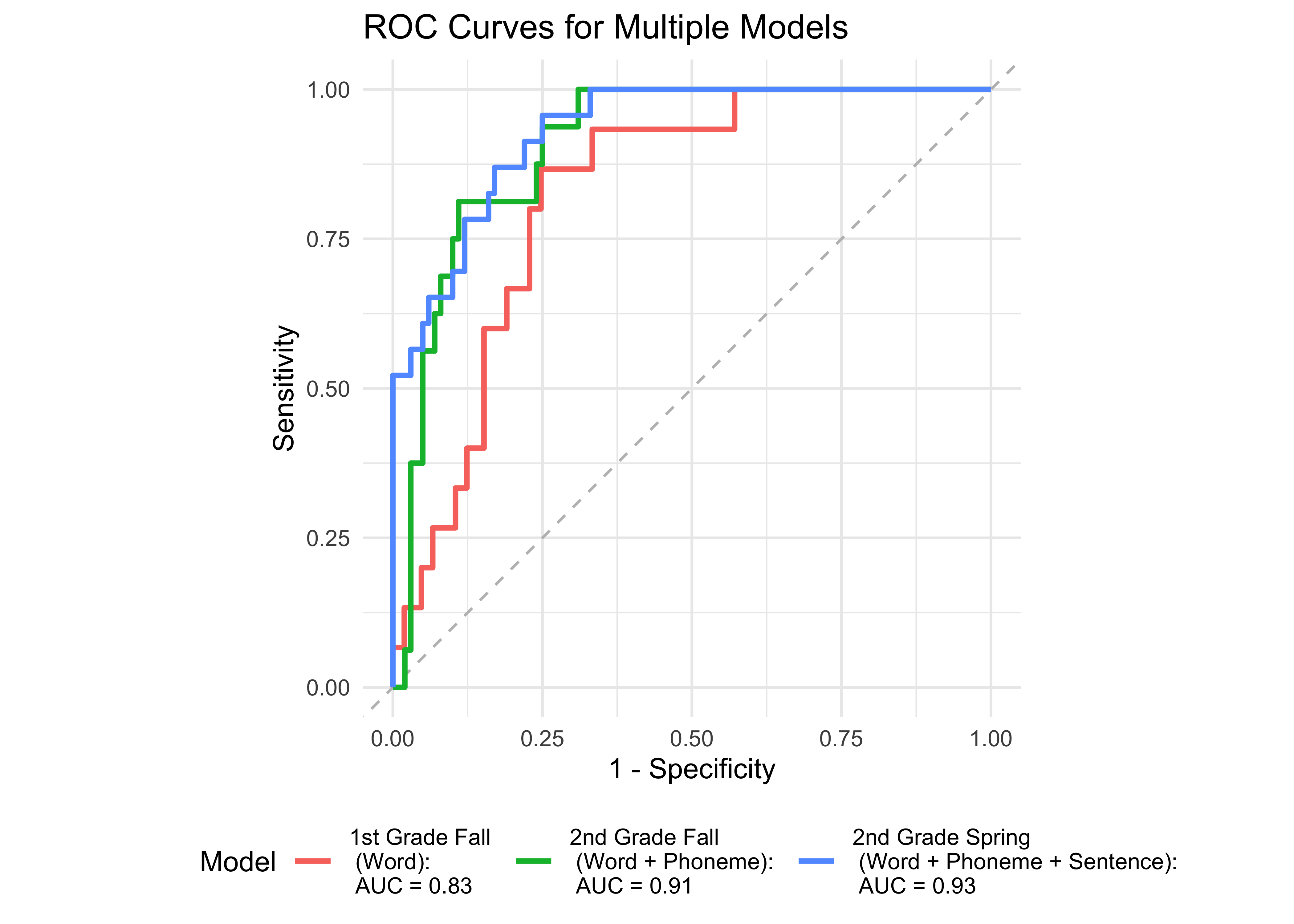
We implemented our ROAR measures beginning in the first grade. As shown in Table 31.1, ROAR-Word administered in first grade consistently predicts third-grade WJ-BRS outcomes.The correlation between ROAR-Word and WJ-BRS strengthens over time. Table 31.2 demonstrates that ROAR measures can predict reading fluency as early as the first grade, with ROAR-Sentence being the most relevant predictor. The highlighted rows indicate the concurrent validity, where the ROAR measures and WJ-BRS were administered within the same month.
| ROAR Measure | ROAR Administration | N | Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|
| ROAR-Word | Fall 2021 | 115 | 0.718 |
| ROAR-Word | Spring 2022 | 117 | 0.739 |
| ROAR-Word | Fall 2022 | 120 | 0.716 |
| ROAR-Word | Spring 2023 | 136 | 0.729 |
| ROAR-Word | Fall 2023 | 156 | 0.744 |
| ROAR-Phoneme | Spring 2022 | 72 | 0.339 |
| ROAR-Phoneme | Fall 2022 | 114 | 0.496 |
| ROAR-Phoneme | Spring 2023 | 129 | 0.591 |
| ROAR-Phoneme | Fall 2023 | 157 | 0.516 |
| ROAR-Sentence | Spring 2023 | 120 | 0.807 |
| ROAR-Sentence | Fall 2023 | 155 | 0.835 |
Based on the WJ-BRS, 32 out of 170 students were identified as high-risk or at-risk struggling readers (scoring below the 50th percentile of the WJ-BRS norms). We treated this classification as the true score. Next, we examined the prediction accuracy of a logistic regression model using ROAR measures taken in the previous year. Figure 31.1 provides further evidence supporting the high sensitivity and specificity of ROAR-Word in predicting dyslexia classification with a lead time of two years.
31.3 Study 2 (Grades 1-3): Fall to Spring prediction of FAST™ earlyReading and FAST™ CBMreading
In a second study we assessed predictive validity of ROAR Foundational Reading Skills measures administered in the Fall and Winter for predicting individually administered FAST™ earlyReading and FAST™ CBMreading in the Spring (for concurrent validity of ROAR Spring assessment see Chapter 29).
31.3.1 Fall ROAR measures predict Spring FAST™ earlyReading and FAST™ CBMreading
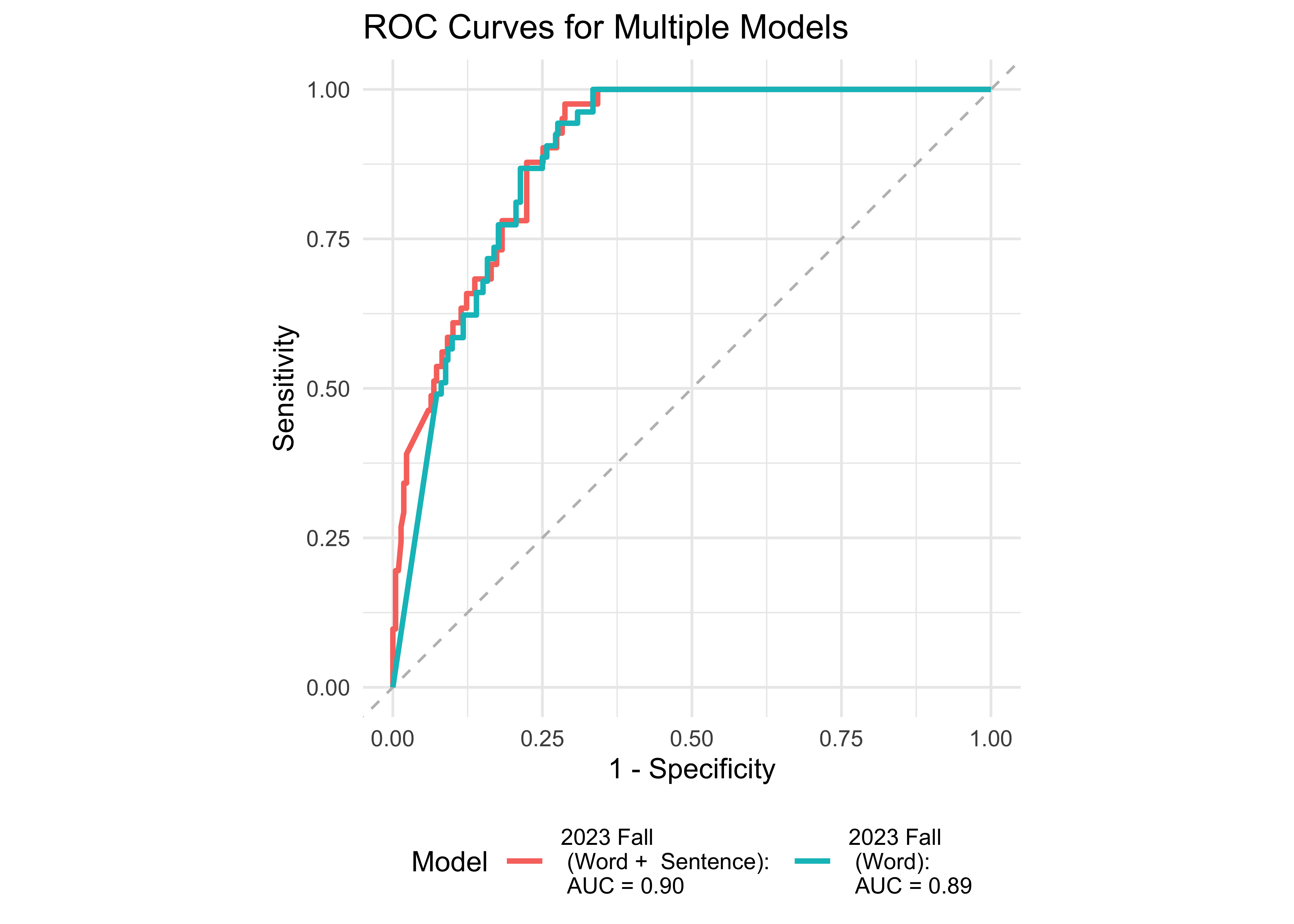
Table 31.3 demonstrates that ROAR-Word in the Fall, among ROAR measures, is the strongest predictor of FAST™ CBMreading performance in the Spring for 1st graders. For 2nd and 3rd graders, both ROAR-Word and ROAR-Sentence are strong predictors of FAST™ CBMreading outcomes. Additionally, Table 31.4 provides further evidence that ROAR-Word in the Fall is a robust predictor of FAST™ earlyReading performance in the Spring. The highlighted rows indicate the concurrent validity, where the ROAR measures and FAST™ were administered within the same month.
| Grade | ROAR Measure | ROAR Administration | N | Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ROAR-Word | Fall 2023 | 309 | 0.725 |
| 1 | ROAR-Word | 2024 Winter | 332 | 0.781 |
| 1 | ROAR-Word | Spring 2024 | 301 | 0.778 |
| 1 | ROAR-Phoneme | Fall 2023 | 301 | 0.585 |
| 1 | ROAR-Phoneme | 2024 Winter | 348 | 0.649 |
| 1 | ROAR-Phoneme | Spring 2024 | 326 | 0.611 |
| 1 | ROAR-Sentence | Fall 2023 | 259 | 0.642 |
| 1 | ROAR-Sentence | 2024 Winter | 341 | 0.791 |
| 1 | ROAR-Sentence | Spring 2024 | 303 | 0.794 |
| 2 | ROAR-Word | Fall 2023 | 335 | 0.752 |
| 2 | ROAR-Word | 2024 Winter | 330 | 0.705 |
| 2 | ROAR-Word | Spring 2024 | 311 | 0.690 |
| 2 | ROAR-Phoneme | Fall 2023 | 343 | 0.501 |
| 2 | ROAR-Phoneme | 2024 Winter | 146 | 0.391 |
| 2 | ROAR-Sentence | Fall 2023 | 326 | 0.764 |
| 2 | ROAR-Sentence | 2024 Winter | 323 | 0.780 |
| 2 | ROAR-Sentence | Spring 2024 | 315 | 0.780 |
| 3 | ROAR-Word | Fall 2023 | 182 | 0.600 |
| 3 | ROAR-Word | 2024 Winter | 156 | 0.596 |
| 3 | ROAR-Word | Spring 2024 | 142 | 0.615 |
| 3 | ROAR-Phoneme | Fall 2023 | 183 | 0.368 |
| 3 | ROAR-Phoneme | 2024 Winter | 95 | 0.380 |
| 3 | ROAR-Sentence | Fall 2023 | 180 | 0.586 |
| 3 | ROAR-Sentence | 2024 Winter | 156 | 0.597 |
| 3 | ROAR-Sentence | Spring 2024 | 141 | 0.598 |
| Grade | ROAR Measure | ROAR Administration | N | Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ROAR-Word | Fall 2023 | 310 | 0.677 |
| 1 | ROAR-Word | 2024 Winter | 332 | 0.756 |
| 1 | ROAR-Word | Spring 2024 | 301 | 0.759 |
| 1 | ROAR-Phoneme | Fall 2023 | 302 | 0.613 |
| 1 | ROAR-Phoneme | 2024 Winter | 348 | 0.671 |
| 1 | ROAR-Phoneme | Spring 2024 | 326 | 0.628 |
| 1 | ROAR-Sentence | Fall 2023 | 259 | 0.562 |
| 1 | ROAR-Sentence | 2024 Winter | 341 | 0.739 |
| 1 | ROAR-Sentence | Spring 2024 | 303 | 0.753 |
We examined the prediction accuracy of a logistic regression model using ROAR measures from Fall 2023 to predict the FAST™ classification (low risk vs. some risk and high risk) in Spring 2024. Figure 31.2 provides evidence supporting the high sensitivity and specificity of ROAR-Word in predicting dyslexia classification in both 1st and 2nd grades. Additionally, ROAR-Phoneme is more useful in 1st grade and ROAR-Sentence proves to be more useful in 2nd grade.
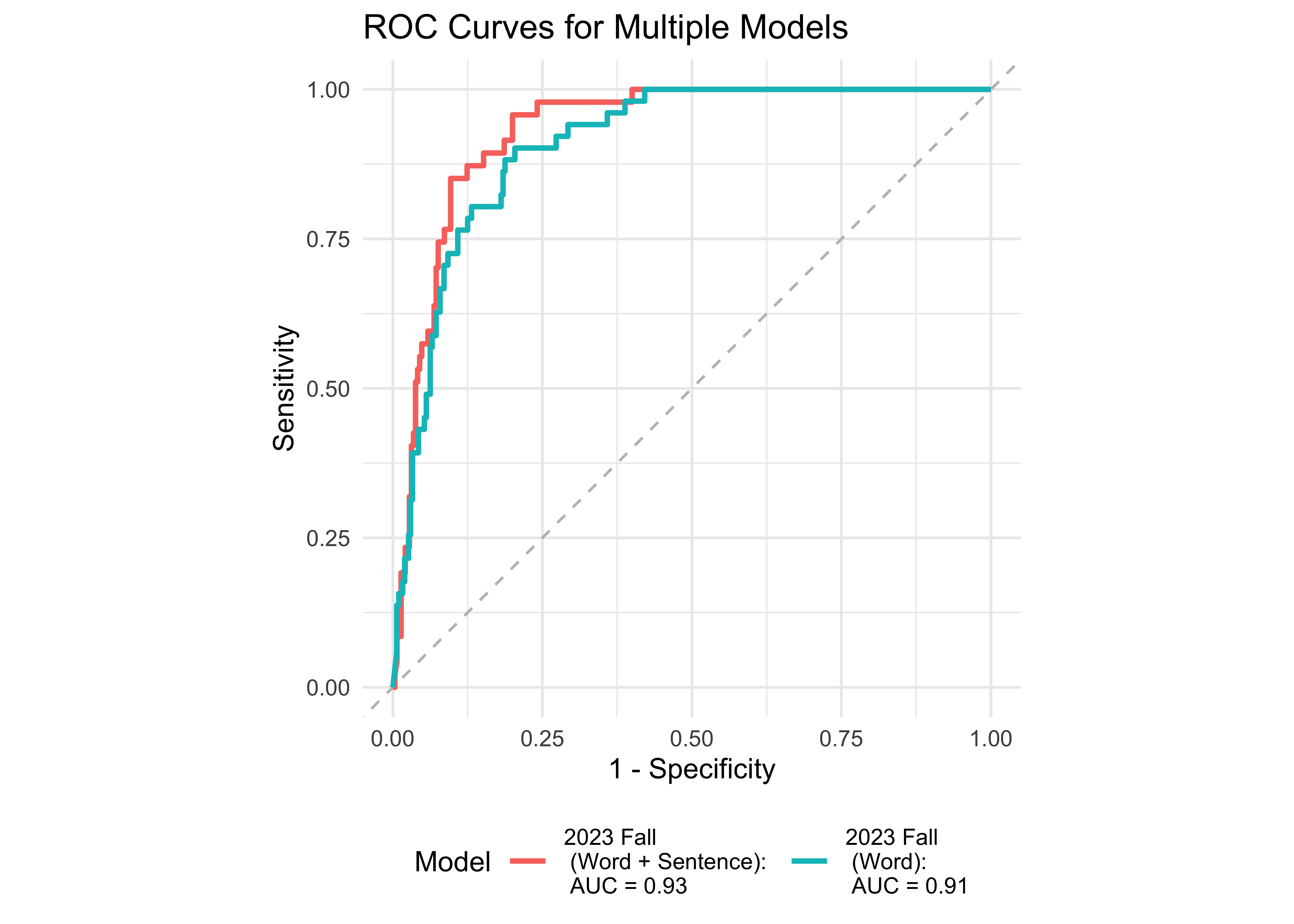
We examined the prediction accuracy of a logistic regression model using ROAR measures from Fall 2023 to predict the FAST™ classification (low risk vs. some risk and high risk) in Spring 2024. Figure 31.3 provides evidence supporting the high sensitivity and specificity of ROAR-Word in predicting dyslexia risk classification in 3rd grade.
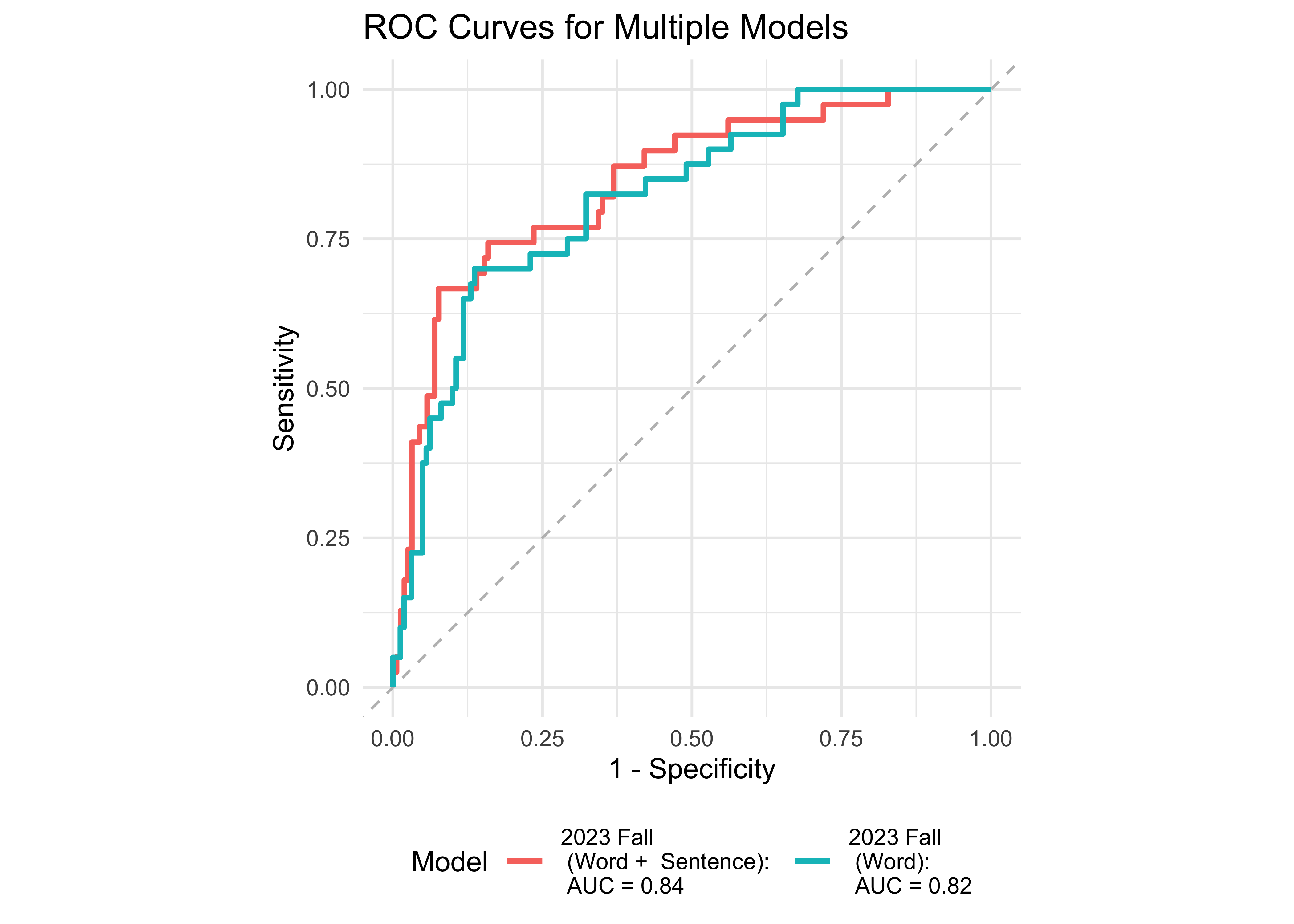
31.3.2 Fall ROAR Composite predicts Spring FAST™ earlyReading and FAST™ CBMreading
The overall ROAR Composite Score is an IRT-based composite using the Letter, Word, and Phoneme measures. In this section, we assessed predictive validity of the ROAR Foundational Reading Skills Composite Score for predicting individually administered FAST™ earlyReading and FAST™ CBMreading in the Spring (for concurrent validity of ROAR Spring assessment see Chapter 29).
Table 31.5 demonstrates that the ROAR Composite Score in Fall 2023-24 and Winter 2023-24, appears to be a strong predictor of FAST™ CBMreading performance in Spring 2023-24 for 1st and 2nd graders (correlation > 0.7). The lower correlations in 3rd grade are likely due to the smaller sample size. Additionally, Table 31.6 provides further evidence that the ROAR Composite Score in Fall 2023-24 and Winter 2023-24, appears to be a strong predictor of FAST™ earlyReading performance in the Spring. The highlighted rows indicate the concurrent validity, where the ROAR measures and FAST™ were administered within the same month.
| Grade | ROAR Administration | N | Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fall 2023-24 | 333 | 0.757 |
| 1 | Winter 2023-24 | 241 | 0.805 |
| 1 | Spring 2023-24 | 315 | 0.761 |
| 2 | Fall 2023-24 | 314 | 0.719 |
| 2 | Winter 2023-24 | 221 | 0.700 |
| 2 | Spring 2023-24 | 277 | 0.672 |
| 3 | Fall 2023-24 | 118 | 0.611 |
| 3 | Winter 2023-24 | 89 | 0.571 |
| 3 | Spring 2023-24 | 88 | 0.594 |
| Grade | ROAR Administration | N | Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fall 2023-24 | 333 | 0.731 |
| 1 | Winter 2023-24 | 240 | 0.804 |
| 1 | Spring 2023-24 | 314 | 0.756 |
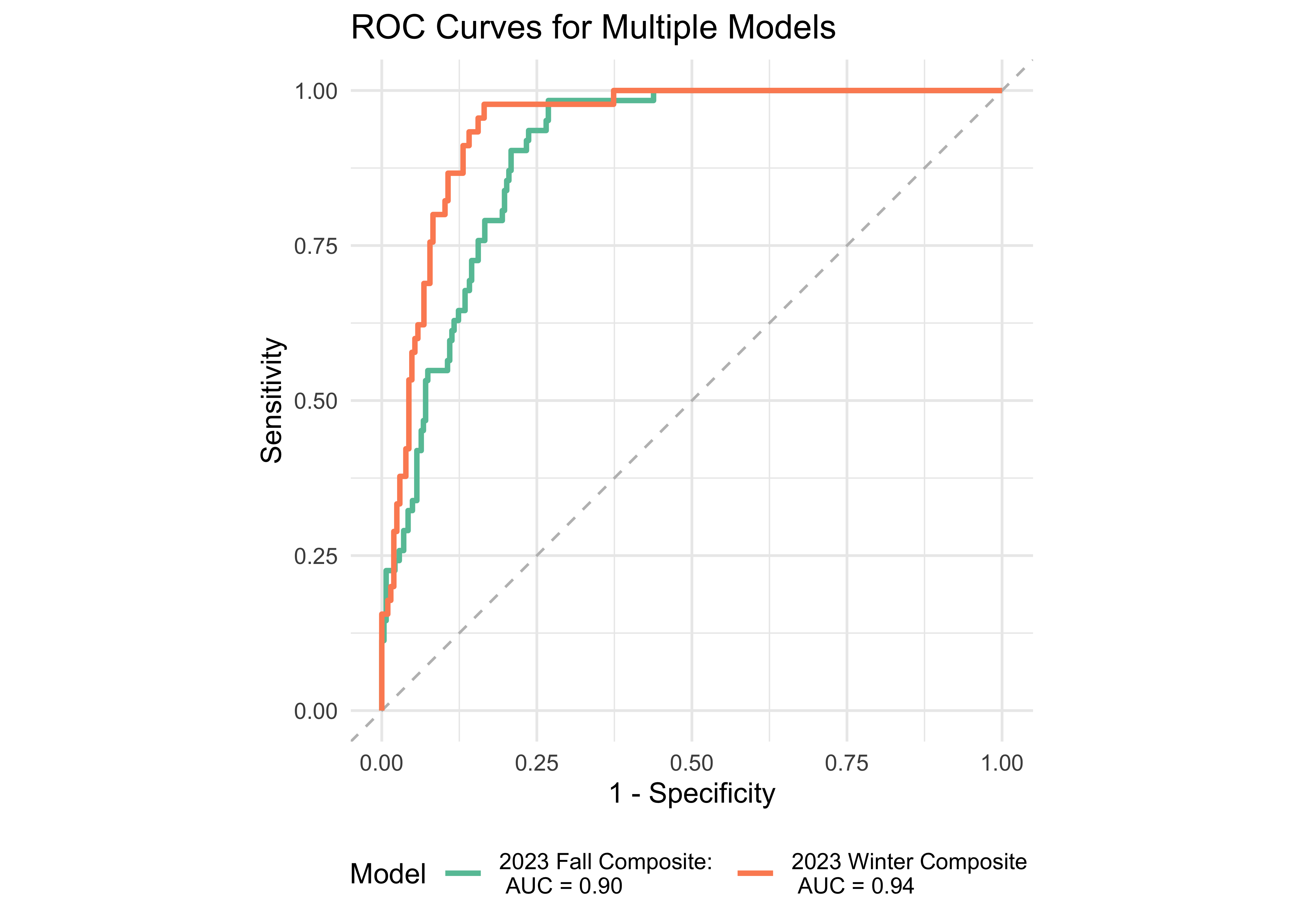
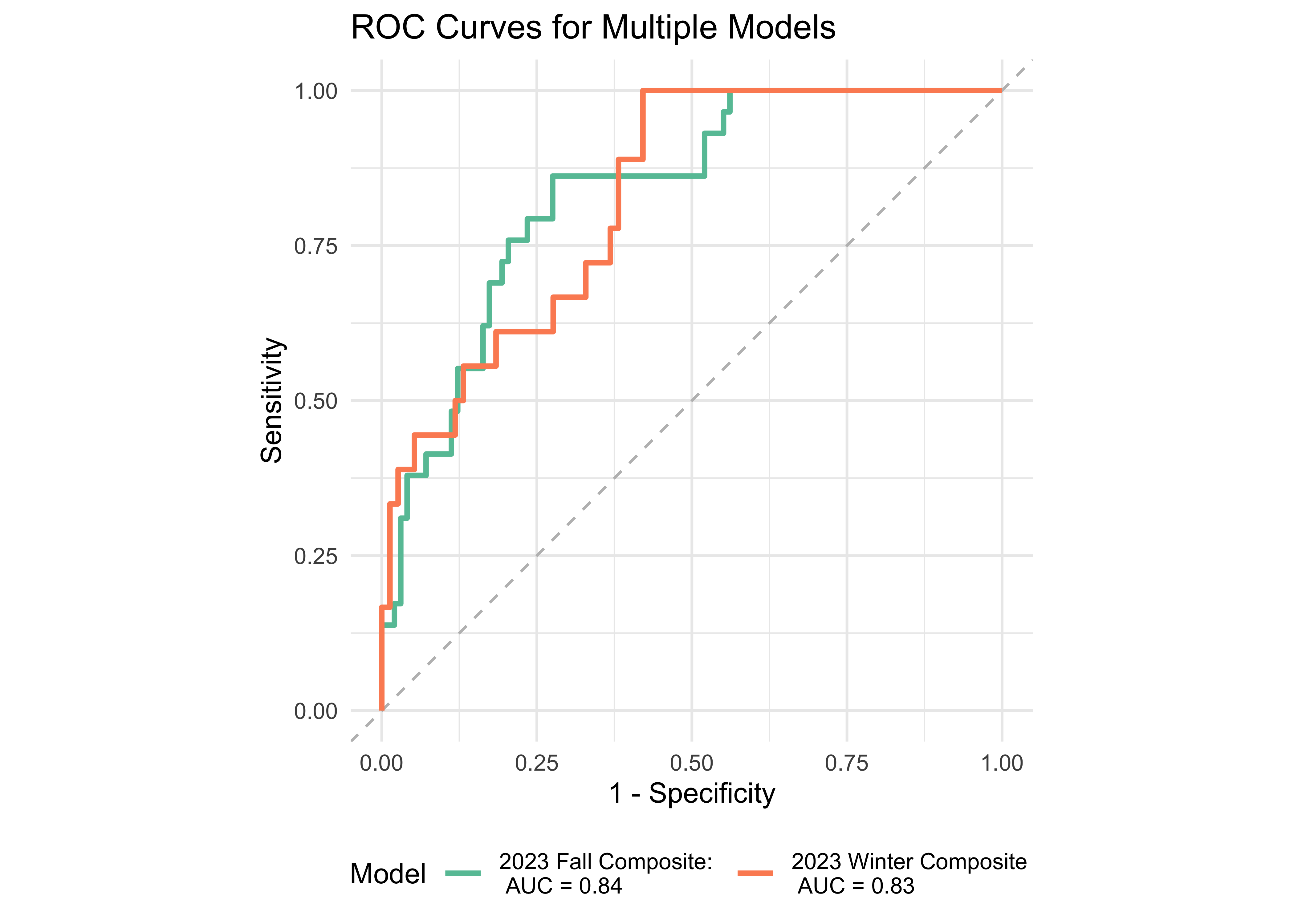
We examined the prediction accuracy of a logistic regression model using the computed ROAR Composite Score from Fall 2023 to predict the FAST™ classification (low risk vs. some risk and high risk) in Spring 2024. Figure 31.4 provides evidence supporting the high sensitivity and specificity of the ROAR Composite Score in predicting dyslexia classification in both 1st and 2nd grades.
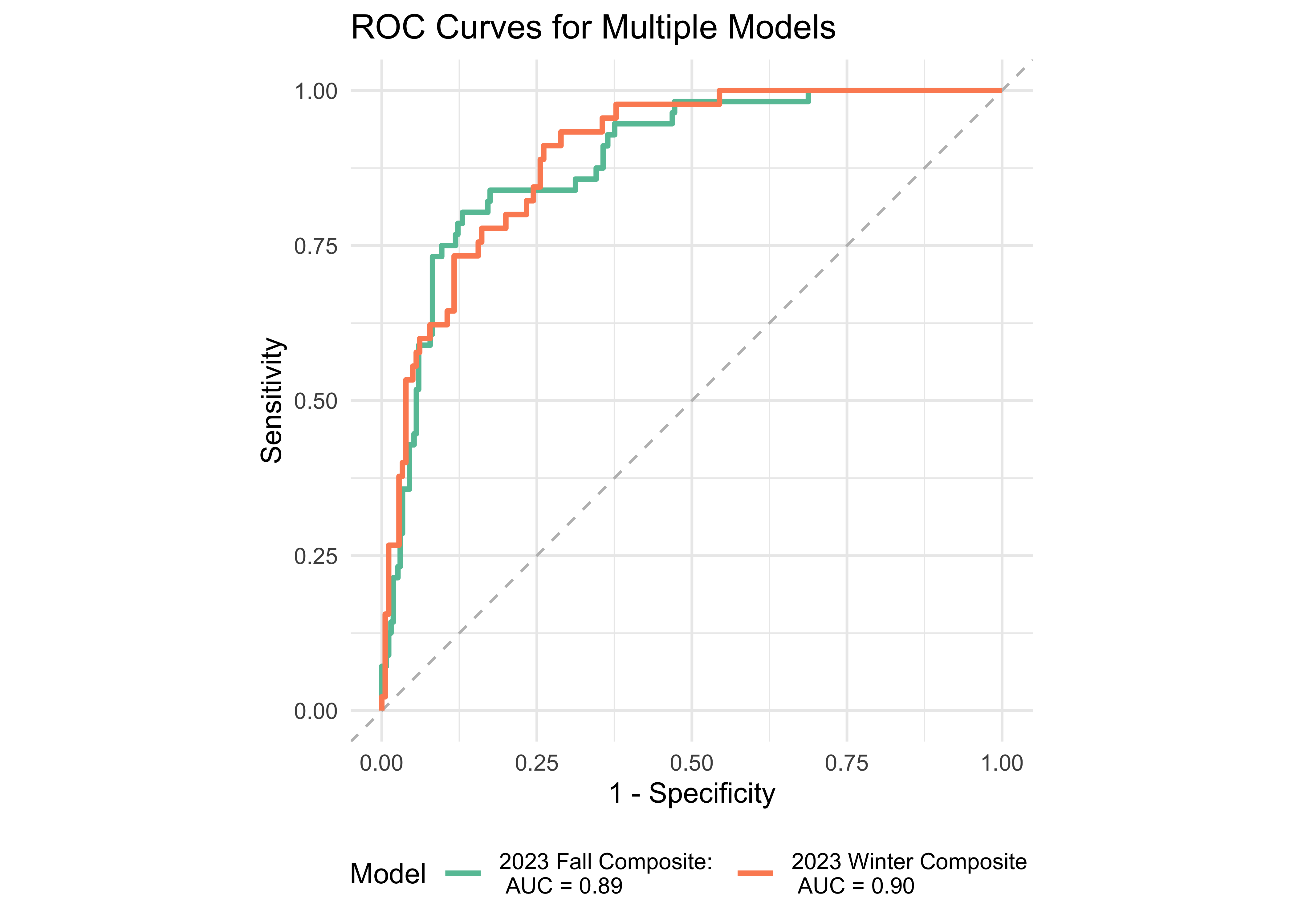
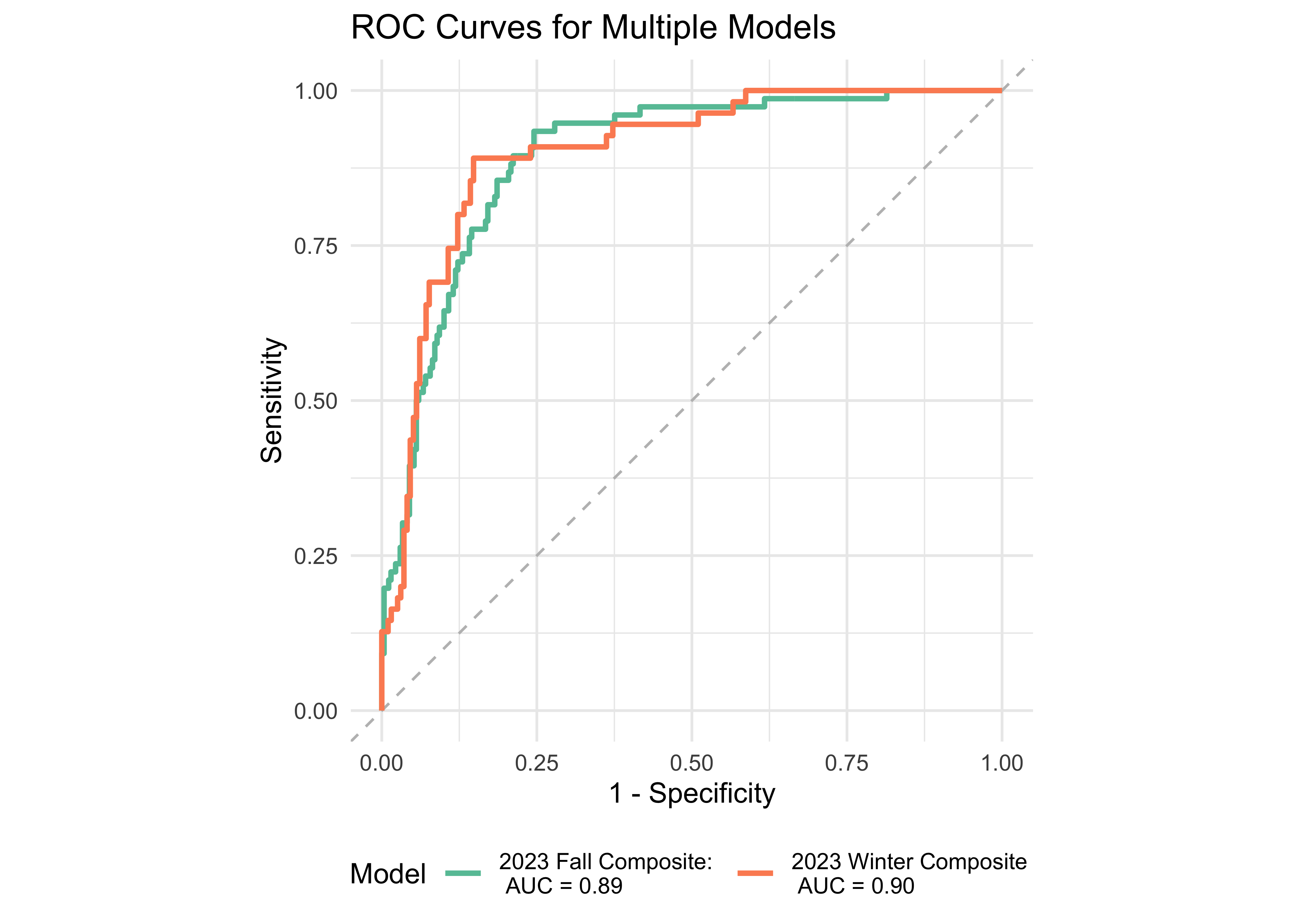
We examined the prediction accuracy of a logistic regression model using ROAR measures from Fall 2023 to predict the FAST™ classification (low risk vs. some risk and high risk) in Spring 2024. Figure 31.5 provides evidence supporting the high sensitivity and specificity of the computed ROAR Composite Score in predicting dyslexia risk classification in 3rd grade.
31.4 Study 3 (Grades K-2): K-2 Screening for reading difficulties with Woodcock Johnson Basic Reading Skills
Through a research collaboration with a large, diverse and representative district in California, we implemented the ROAR Foundational Reading Skills Suite universally for Kindergarten, 1st, and 2nd grade. The students completed ROAR measures in the Spring of 2024 (2023/24 school year), Fall of 2024, and Spring of 2025 (2024/25 school year).
In the Spring of 2025, students were individually administered Woodcock Johnson Letter Word Identification and Word Attack subtest to calculate the Basic Reading Skills Composite score. This standardized score is the most widely used measure in dyslexia research and practice.
31.4.1 Using ROAR measures to screeen for reading difficulties with Woodcock Johnson Basic Reading Skills
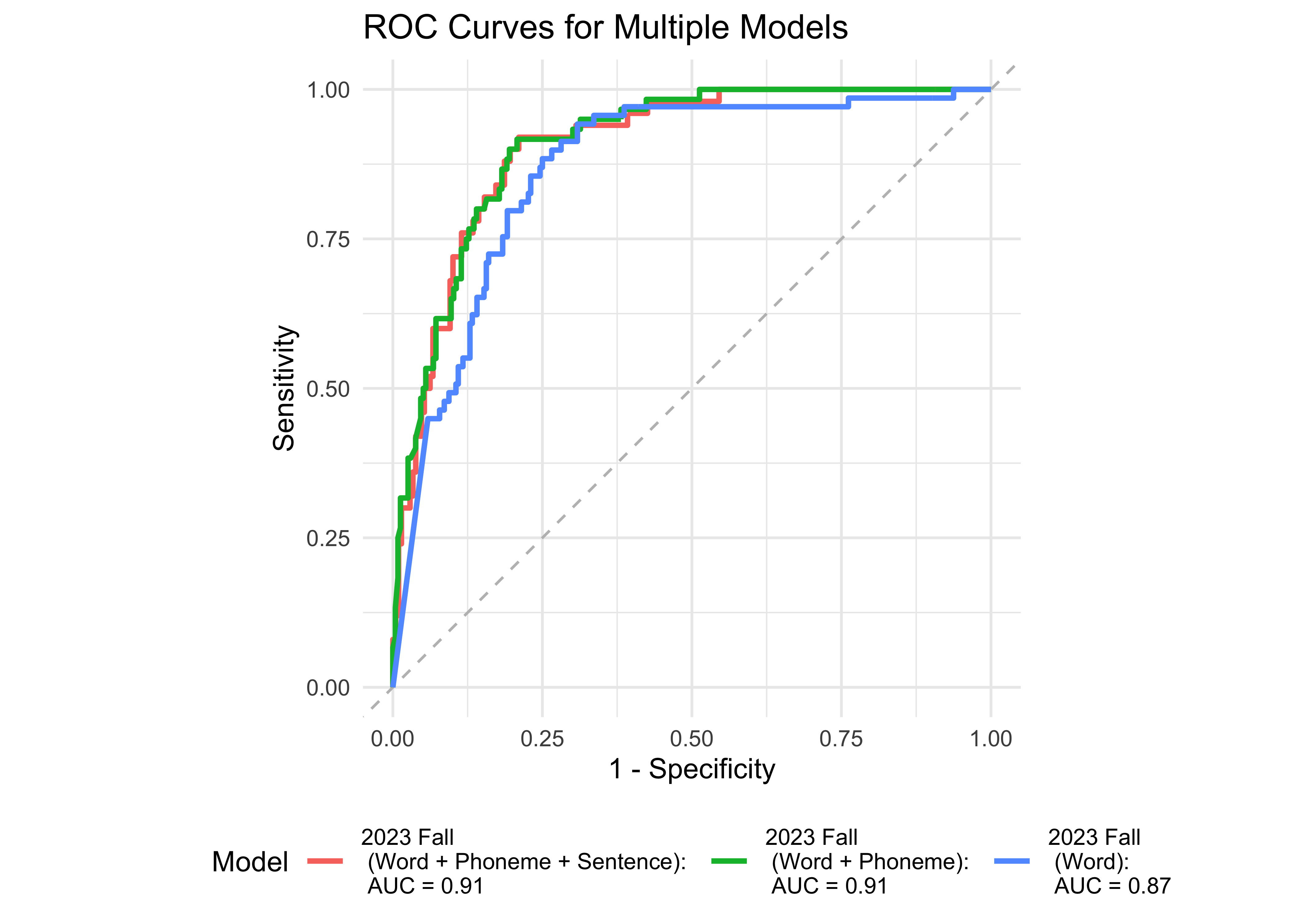
As shown in Table 31.7, Table 31.8, and Table 31.9 ROAR-Word administered across grades K-2 consistently predicts WJ-BRS outcomes. The highlighted rows indicate the concurrent validity, where the ROAR measures and validation (i.e., WJ-BRS and DIBELS-ORF) were administered within the same month.
| ROAR Measure | ROAR Administration | N | Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|
| ROAR Word | Fall 2024 | 6 | NA |
| ROAR Word | Spring 2025 | 226 | 0.503 |
| ROAR Phoneme | Fall 2024 | 280 | 0.610 |
| ROAR Phoneme | Spring 2025 | 269 | 0.648 |
| ROAR Sentence | Fall 2024 | 3 | NA |
| ROAR Sentence | Spring 2025 | 77 | 0.653 |
| ROAR Letter | Fall 2024 | 291 | 0.530 |
| ROAR Letter | Spring 2025 | 291 | 0.555 |
| ROAR Measure | ROAR Administration | N | Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|
| ROAR Word | Spring 2024 | 19 | NA |
| ROAR Word | Fall 2024 | 197 | 0.650 |
| ROAR Word | Spring 2025 | 207 | 0.760 |
| ROAR Phoneme | Spring 2024 | 82 | 0.531 |
| ROAR Phoneme | Fall 2024 | 2 | NA |
| ROAR Phoneme | Spring 2025 | 204 | 0.595 |
| ROAR Sentence | Spring 2024 | 6 | NA |
| ROAR Sentence | Fall 2024 | 130 | 0.625 |
| ROAR Sentence | Spring 2025 | 168 | 0.720 |
| ROAR Letter | Spring 2024 | 93 | 0.325 |
| ROAR Letter | Fall 2024 | 2 | NA |
| ROAR Letter | Spring 2025 | 193 | 0.289 |
| ROAR Measure | ROAR Administration | N | Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|
| ROAR Word | Spring 2024 | 114 | 0.778 |
| ROAR Word | Fall 2024 | 281 | 0.748 |
| ROAR Word | Spring 2025 | 260 | 0.782 |
| ROAR Phoneme | Spring 2024 | 67 | 0.604 |
| ROAR Phoneme | Fall 2024 | 3 | NA |
| ROAR Phoneme | Spring 2025 | 275 | 0.632 |
| ROAR Sentence | Spring 2024 | 96 | 0.698 |
| ROAR Sentence | Fall 2024 | 233 | 0.690 |
| ROAR Sentence | Spring 2025 | 231 | 0.641 |
| ROAR Letter | Spring 2024 | 63 | 0.360 |
| ROAR Letter | Spring 2025 | 282 | 0.215 |
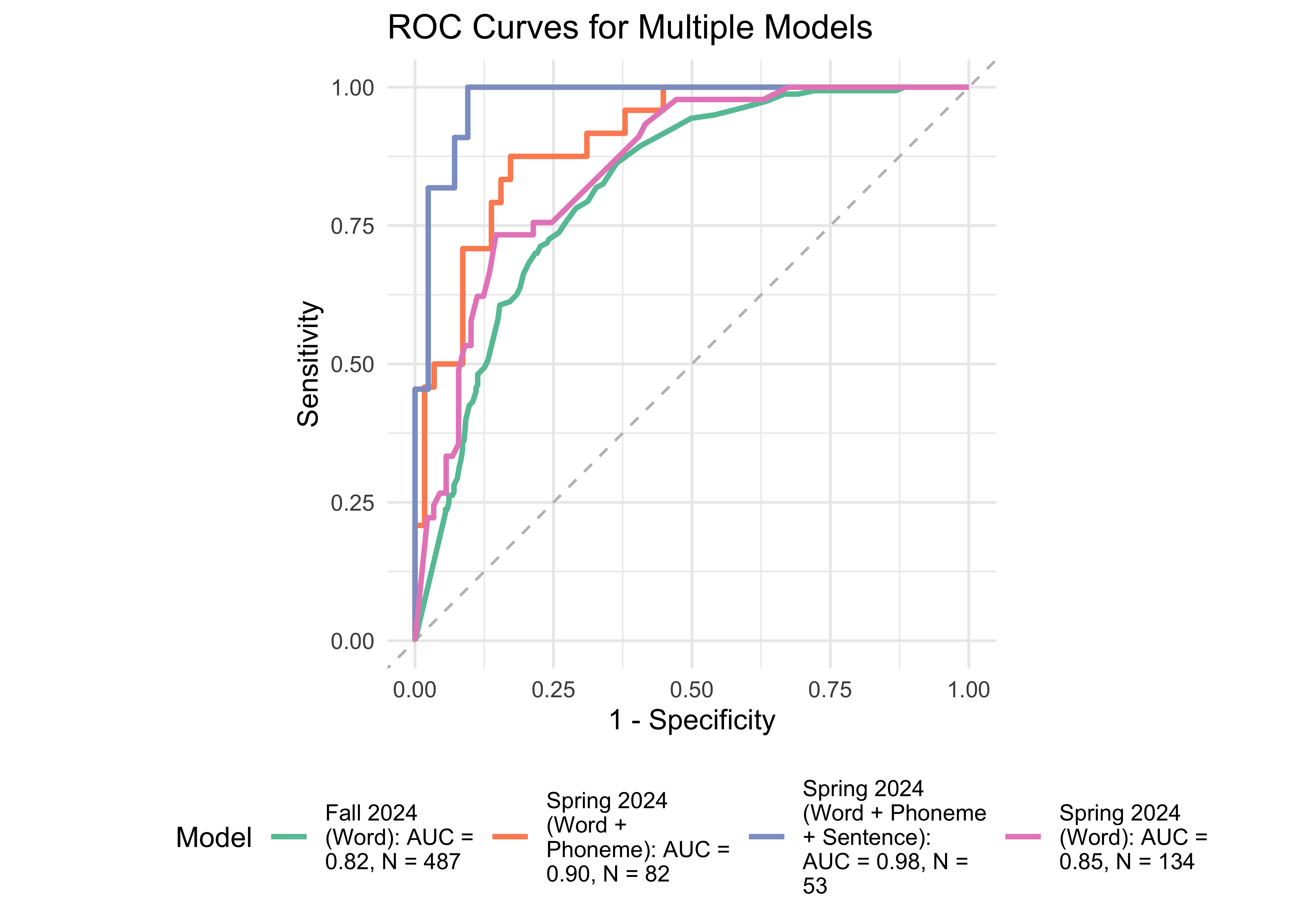
Based on WJ-BRS classifications, 327 out of 796 students were identified as high-risk or at-risk (scoring below the 50th percentile of the WJ-BRS norms). We treated this classification as the true score. Next, we examined the prediction accuracy of a logistic regression model using ROAR measures taken in the previous year. Figure 31.6 provides further evidence supporting the high sensitivity and specificity of ROAR-Word in predicting dyslexia classification with a lead time of one year.
31.4.2 Using ROAR Composite to screeen for reading difficulties with Woodcock Johnson Basic Reading Skills
As previously mentioned, the overall ROAR Composite Score is an IRT-based composite using the Letter, Word, and Phoneme measures. In this section, we assessed predictive validity of the ROAR Foundational Reading Skills Composite Score from previous timepoints for predicting individually administered Woodcock Johnson in Spring 2025.
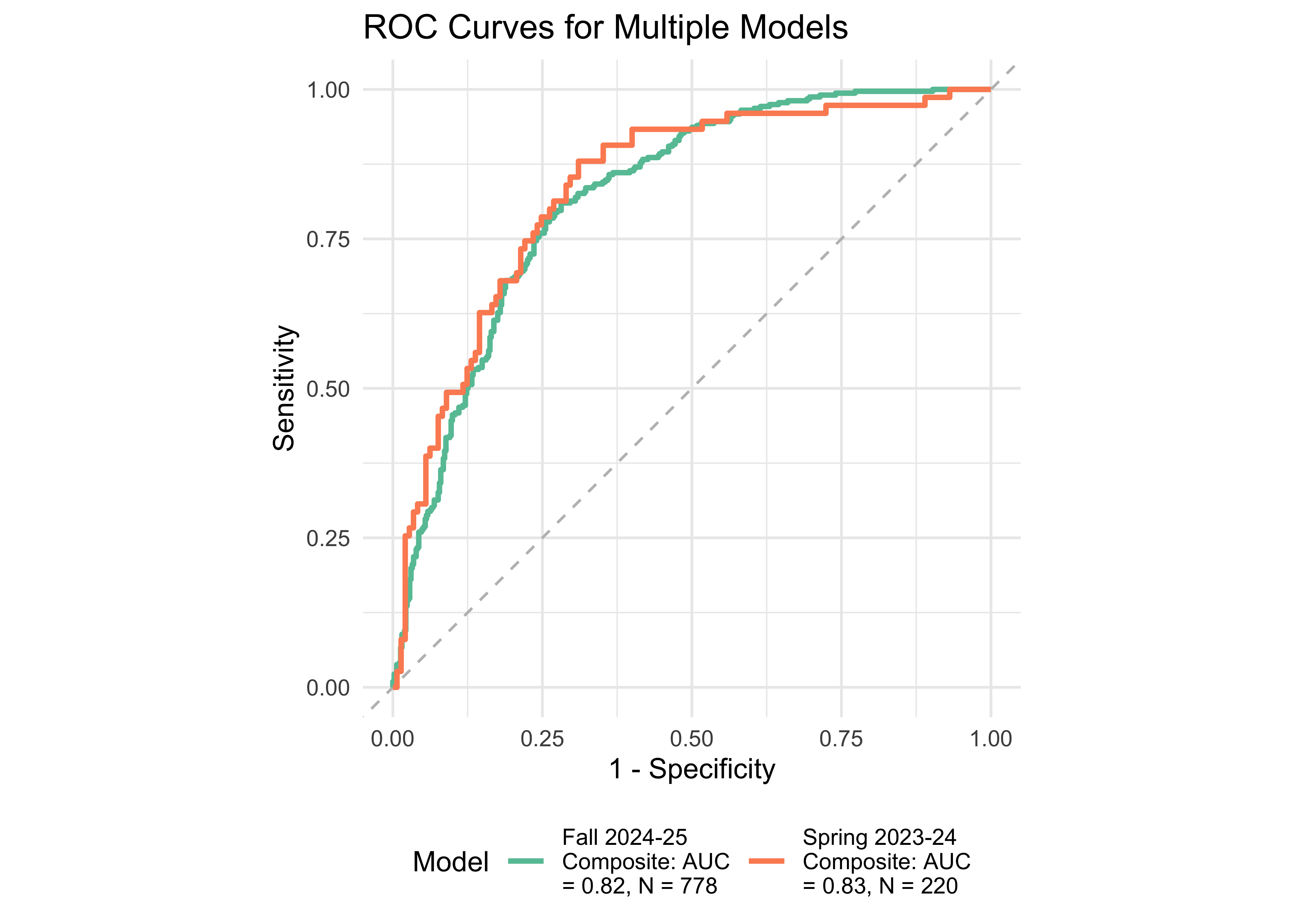
As shown in Table 31.10, Table 31.11, and Table 31.12 the calculated ROAR Composite Score across grades K-2 consistently predicts WJ-BRS outcomes. The highlighted rows indicate the concurrent validity, where the ROAR measures and validation (i.e., WJ-BRS and DIBELS-ORF) were administered within the same month.
| ROAR Administration | N | Correlation |
|---|---|---|
| Fall 2024-25 | 293 | 0.601 |
| Spring 2024-25 | 291 | 0.683 |
| ROAR Administration | N | Correlation |
|---|---|---|
| Spring 2023-24 | 93 | 0.467 |
| Fall 2024-25 | 199 | 0.656 |
| Spring 2024-25 | 213 | 0.759 |
| ROAR Administration | N | Correlation |
|---|---|---|
| Spring 2023-24 | 126 | 0.772 |
| Fall 2024-25 | 283 | 0.750 |
| Spring 2024-25 | 280 | 0.762 |
31.5 Study 4 (Grades K-2): Screening for reading difficulties with DIBELS Oral Reading Fluency (ORF)
31.5.1 Using ROAR measures to screeen for reading difficulties with DIBELS Oral Reading Fluency
The same cohort of students reported in Section 31.4 were also administered DIBELS Oral Reading Fluency (ORF) in the Spring of 2025. Table 31.13 demonstrates that ROAR measures predict ORF more than one school year into the future. The highlighted rows indicate the concurrent validity, where the ROAR measures and validation (i.e., WJ-BRS and DIBELS-ORF) were administered within the same month.
| ROAR Measure | ROAR Administration | N | Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|
| ROAR Word | Spring 2023 | 132 | 0.556 |
| ROAR Word | Fall 2024 | 471 | 0.613 |
| ROAR Word | Spring 2025 | 462 | 0.668 |
| ROAR Phoneme | Spring 2023 | 145 | 0.541 |
| ROAR Phoneme | Fall 2024 | 5 | NA |
| ROAR Phoneme | Spring 2025 | 472 | 0.548 |
| ROAR Sentence | Spring 2023 | 101 | 0.368 |
| ROAR Sentence | Fall 2024 | 362 | 0.462 |
| ROAR Sentence | Spring 2025 | 399 | 0.609 |
| ROAR Letter | Spring 2023 | 151 | 0.403 |
| ROAR Letter | Fall 2024 | 6 | NA |
| ROAR Letter | Spring 2025 | 466 | 0.230 |
31.5.2 Using ROAR Composite to screeen for reading difficulties with DIBELS Oral Reading Fluency
In this section, we assessed predictive validity of the ROAR Foundational Reading Skills Composite Score from previous timepoints for predicting individually administered DIBELS Oral Reading Fluency in Spring 2025. Table 31.13 demonstrates that the calculated ROAR Composite Score predicts ORF more than one school year into the future. The highlighted rows indicate the concurrent validity, where the ROAR measures and validation (i.e., WJ-BRS and DIBELS-ORF) were administered within the same month.
| ROAR Administration | N | Correlation |
|---|---|---|
| Spring 2023-24 | 215 | 0.551 |
| Fall 2024-25 | 475 | 0.612 |
| Spring 2024-25 | 486 | 0.656 |
31.6 Study 5 (Grade K): Winter to Spring prediction of Woodcock Johnsons Basic Reading Skills (BRS)
31.6.1 Winter ROAR measures predict Spring FAST™ Woodcock Johnson’s Basic Reading Skills
In Winter 2025, students were administered ROAR measures and in the Spring of 2025 were individually administered Woodcock Johnson Letter Word Identification and Word Attack subtests to calculate the Basic Reading Skills Composite score. This standardized score is the most widely used measure in dyslexia research and practice.
As shown in Table 31.15, ROAR-Word and the combination of the ROAR foundational reading assessments (Letter, Word, Phoneme) administered in Kindergarten consistently predicts WJ-BRS outcomes.
| ROAR Measure | ROAR Administration | N | Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|
| ROAR Word | Winter 24-25 | 83 | 0.739 |
| ROAR Phoneme | Winter 24-25 | 94 | 0.593 |
| ROAR Letter | Winter 24-25 | 96 | 0.269 |
| ROAR Composite | Winter 24-25 | 82 | 0.788 |
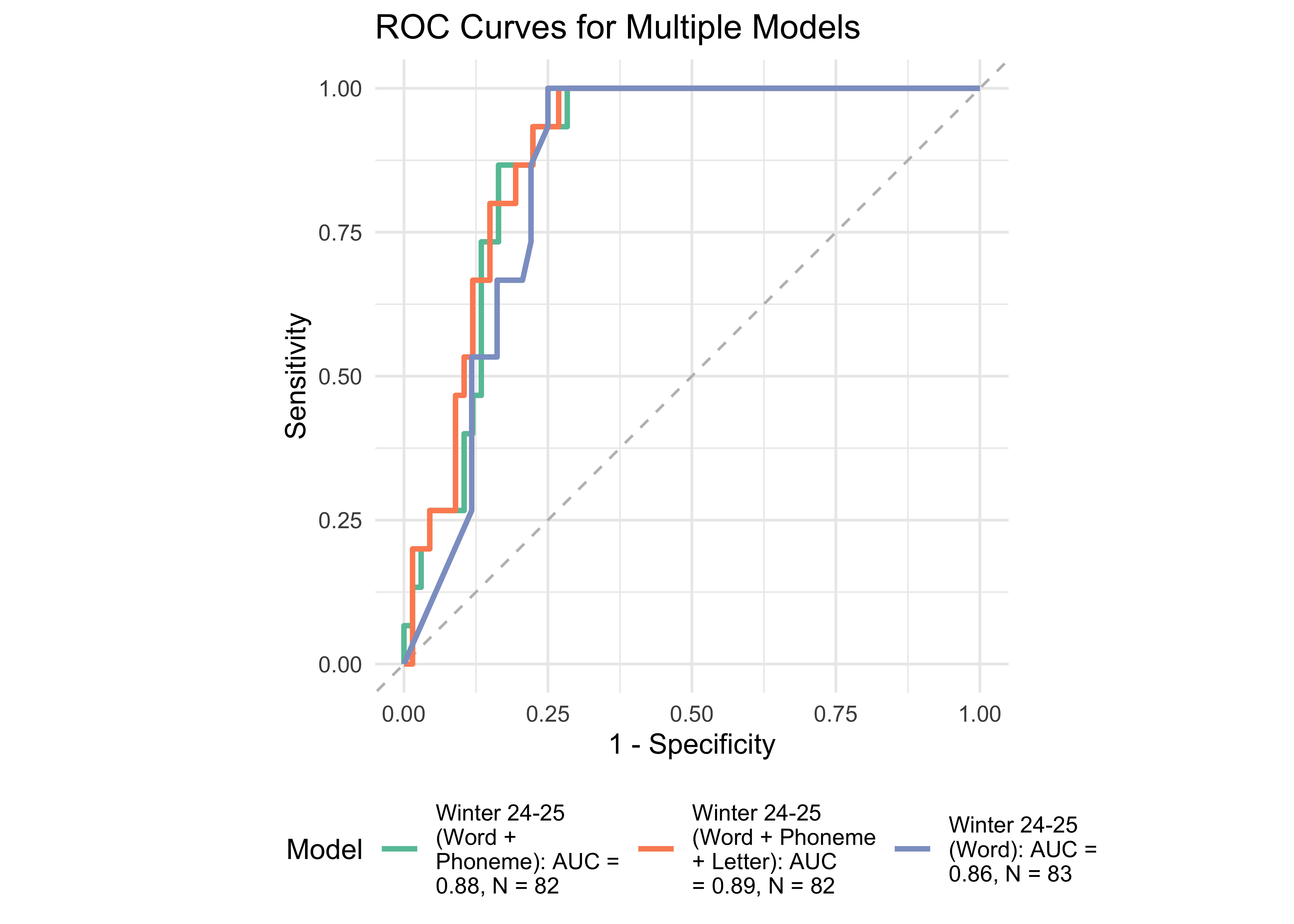
Based on WJ-BRS classifications, 21 out of 96 students were identified as high-risk or at-risk (scoring below the 50th percentile of the WJ-BRS norms). We treated this classification as the true score. Next, we examined the prediction accuracy of a logistic regression model using ROAR measures taken in the previous year. Figure 31.8 provides further evidence supporting the high sensitivity and specificity of ROAR-Word in predicting dyslexia classification with a lead time of ~3-6 months.
31.6.2 Winter ROAR Composite predicts Spring Woodcock Johnson’s Basic Reading Skills
In this section, we assessed predictive validity of the ROAR Foundational Reading Skills Composite Score from Winter 2025 for predicting individually administered WJ BRS in Spring 2025.
As shown in Table 31.16, the computed ROAR Composite Score administered in Kindergarten in Winter 2025 consistently predicts WJ-BRS outcomes in Spring 2025.
| ROAR Administration | N | Correlation |
|---|---|---|
| Winter 2024-25 | 96 | 0.646 |
Based on WJ-BRS classifications, 21 out of 96 students were identified as high-risk or at-risk (scoring below the 50th percentile of the WJ-BRS norms). We treated this classification as the true score. Next, we examined the prediction accuracy of a logistic regression model using ROAR measures taken in the previous year. Figure 31.9 provides further evidence supporting the high sensitivity and specificity of the ROAR Composite Score in predicting dyslexia classification with a lead time of ~3-6 months.
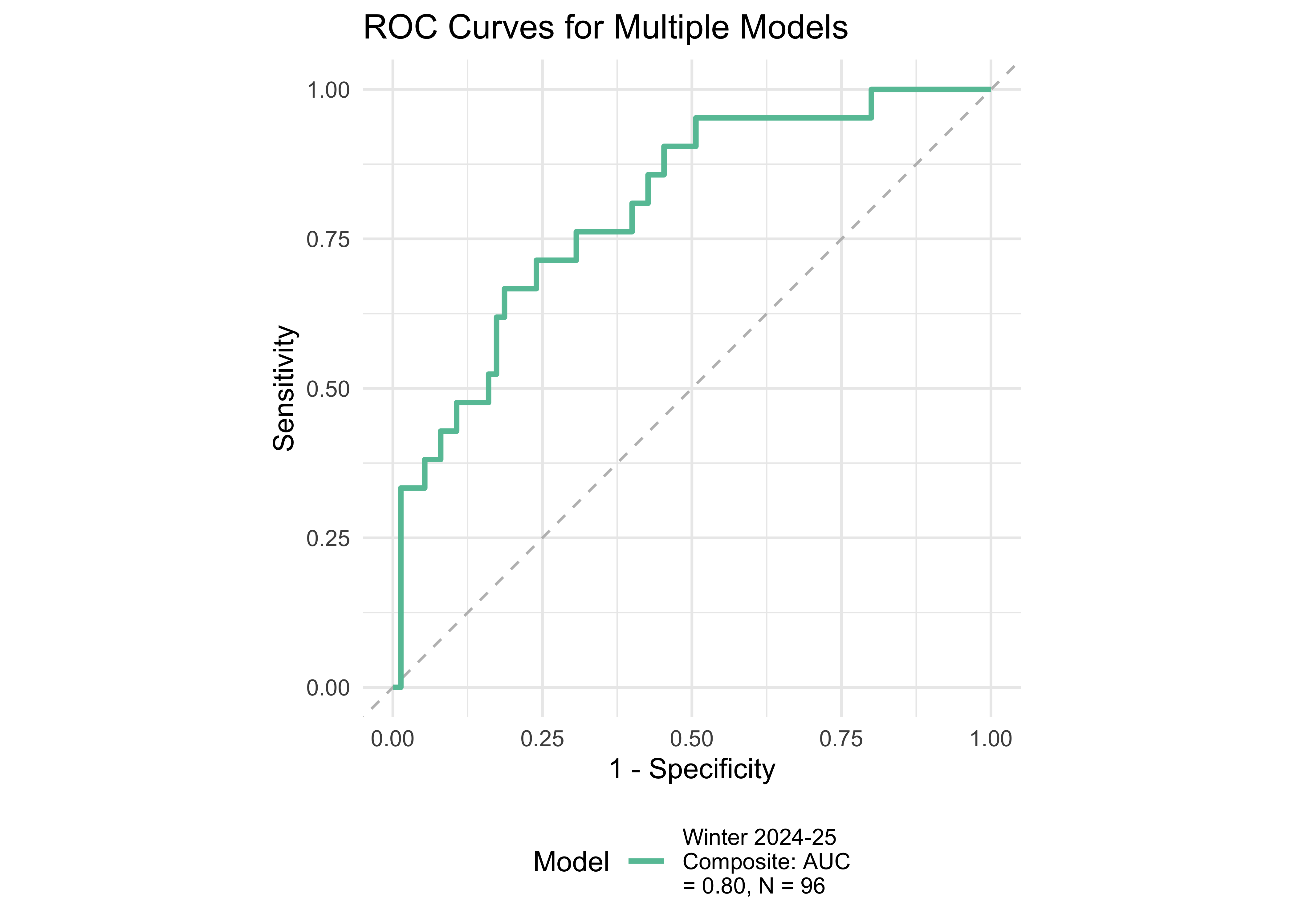
31.7 ROAR Composite Predictive Validity Overview
| Grade | Season | AUC | N | Validation Assessments | Figure Referenced |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | Fall to Spring | 0.601 | 293 | WJ BRS | Table 31.10 |
| K | Winter to Spring | 0.646 | 96 | WJ BRS | Table 31.16 |
| 1 | Fall to Spring | 0.656 | 199 | WJ BRS | Table 31.11 |
| 1 | Fall to Spring | 0.731 | 333 | FastBridge EarlyReading | Table 31.6 |
| 1 | Fall to Spring | 0.757 | 333 | FastBridge CBM | Table 31.5 |
| 2 | Fall to Spring | 0.750 | 283 | WJ BRS | Table 31.12 |
| 2 | Fall to Spring | 0.719 | 314 | FastBridge CBM | Table 31.5 |
| 3 | Fall to Spring | 0.611 | 118 | FastBridge CBM | Table 31.5 |